Business Model Development
What Is a Business Model?
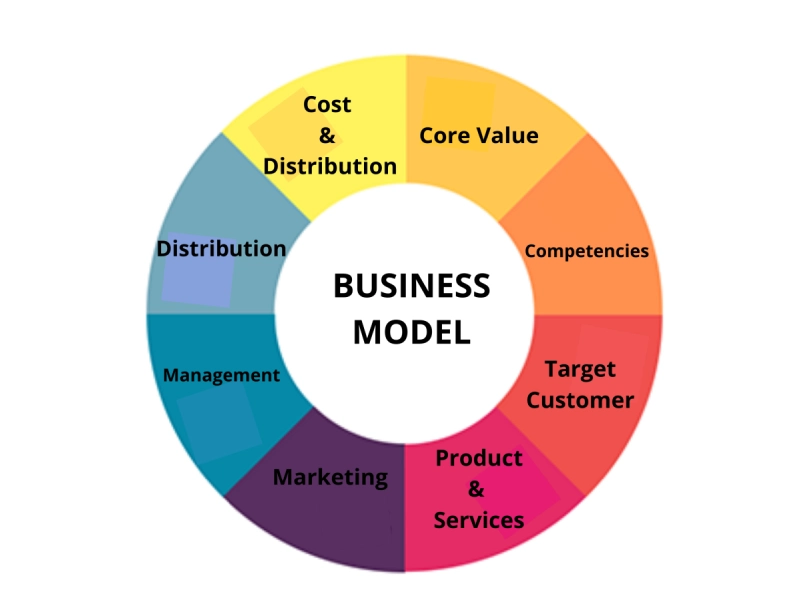
A business model is the strategic framework a company uses to generate profit. It defines the products or services a business offers, its target market, and the expected costs involved. A well-structured business model is crucial for both emerging and established businesses, serving as a foundation for attracting investments, recruiting top talent, and guiding management and employees toward achieving organizational goals.
To remain competitive, businesses must regularly reassess and refine their business models to anticipate future challenges and adapt to changing market dynamics. Additionally, a clear business model provides investors with insights into the company’s growth potential and helps employees understand their role in the company’s vision.
Key Takeaways:
-
- A business model outlines a company’s core strategy for generating sustainable profits.
- It includes information on products or services offered, target markets, and cost structures.
- Success hinges on two primary factors: pricing strategy and cost management.
- Periodic revisions ensure alignment with market trends and customer expectations.
- Investors and analysts often evaluate a company’s business model through metrics like gross profit.
Understanding Business Models
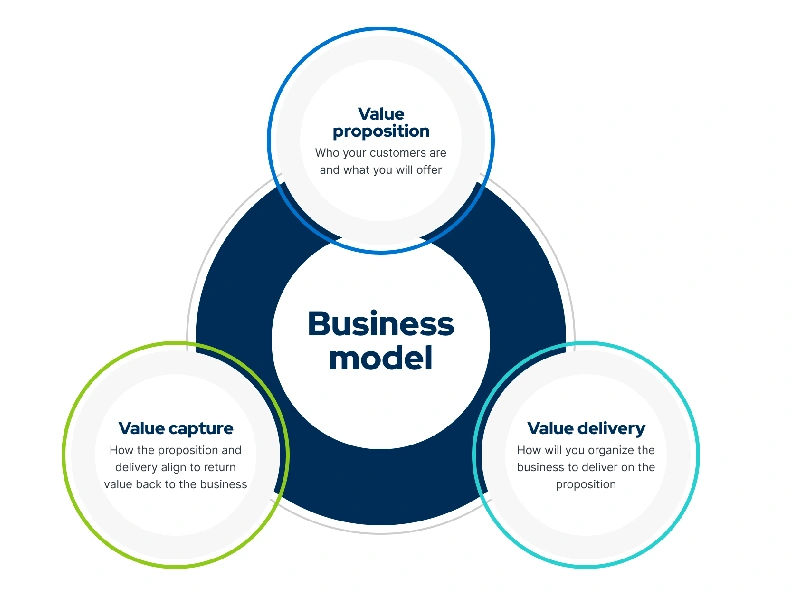
A business model is a high-level strategy for operating profitably in a specific marketplace. It serves as a guide to achieving business goals while attracting investments and talent.
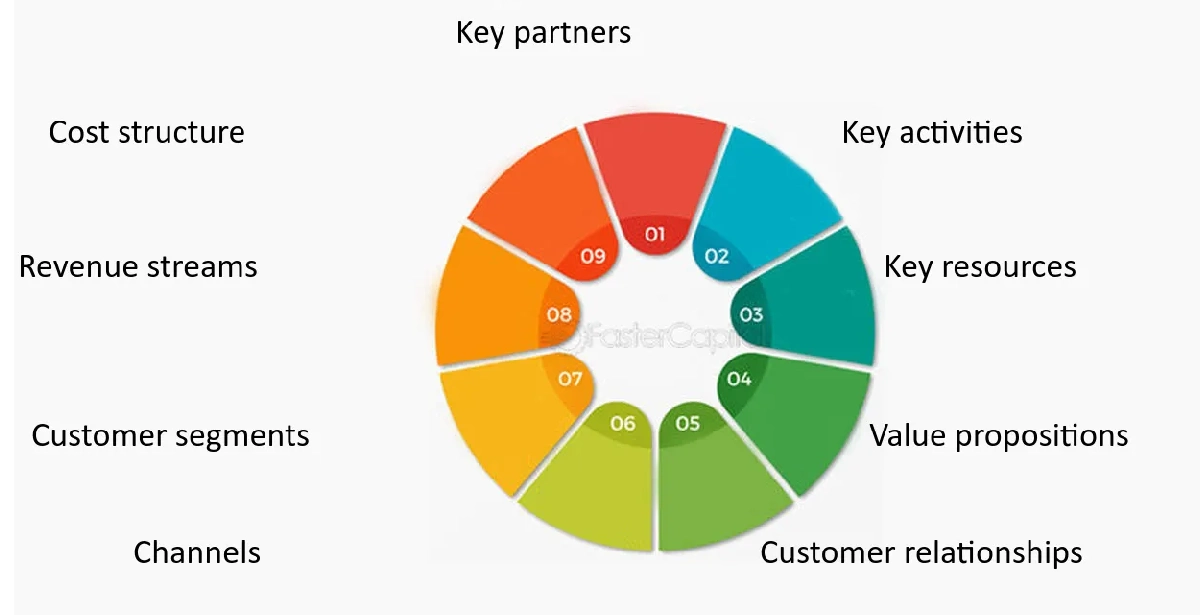
One of the key components of any business model is the value proposition—a clear description of what makes a company’s products or services unique and desirable. This proposition differentiates the business from its competitors and appeals to its target market.
A comprehensive business model should also include:
- Startup costs and financing sources
- Target customer demographics
- Marketing strategies
- Competitor analysis
- Revenue and expense projections
- Potential partnerships
For instance, an advertising agency’s model may highlight mutual benefits from partnerships with printing companies for client referrals, expanding opportunities for growth.
Common Types of Business Models
Business models vary across industries, reflecting different ways of generating revenue. Below are several examples:
1. Retailer
Retailers sell products directly to customers, often purchasing finished goods from manufacturers or distributors.
Example: Costco Wholesale
2. Manufacturer
Manufacturers source raw materials and produce finished goods, which they sell to distributors, retailers, or customers.
Example: Ford Motor Company
3. Fee-for-Service
These businesses provide specialized services for a fee, charging hourly rates or fixed costs for agreements.
Example: DLA Piper LLP
4. Subscription
This model aims to cultivate long-term customer loyalty by offering recurring benefits in exchange for periodic payments.
Example: Spotify
5. Freemium
A freemium model provides basic services for free, enticing customers to upgrade to premium, paid versions for advanced features.
How to Create a Business Model
Crafting a business model tailored to your goals requires a strategic approach. Here are the key steps:
1. Identify Your Audience
Start by defining your target market. Understanding your audience helps you refine your product, messaging, and marketing approach to meet their specific needs.
2. Define the Problem
Identify the core problem your business seeks to solve. Whether it’s providing home repair tools or offering dining experiences, addressing a clear demand is essential for business success.
3. Understand Your Offerings
Outline your products or services in detail. Align your expertise with market needs, tweaking your offerings to create a strong value proposition.
4. Document Your Needs
Identify potential challenges and operational hurdles, including logistics, costs, and market demands. Document these aspects to ensure your business is prepared for launch.
5. Find Key Partners
Build relationships with suppliers, distributors, or collaborators who can complement your business offerings. For instance, event planners may partner with caterers or florists to enhance their services.
6. Set Monetization Strategies
Determine how your business will generate revenue. This could include strategies like direct sales, subscriptions, or partnerships. Clearly define pricing and cost structures for profitability.
7. Test Your Model
Before full-scale implementation, conduct test launches or surveys. Gather feedback to refine pricing, services, and customer experience. Leverage market insights to optimize your model for success.
A strong business model lays the foundation for growth, profitability, and innovation. By continually refining your approach and adapting to change, you can ensure sustainable progress and long-term success.
Retail Consulting
Retail Store Setup
SOP for Retail Store
Setup eCommerce Business
Dark Stores Retail
Develop Franchise Model
Retail Store Business Plan
Retail Management Training
Standard Operating Procedures
Business Plan Services
Industries
Apparel, Fashion Retail
Grocery & Supermarket
Furniture & Furnishings Retail
Luxury Retail Consulting
Healthcare Management
Stationery & Toy Retail
Automobile Dealership
Education Management
E-Commerce Consulting
B2B eCommerce Consulting
Start Dark Store
Start Online Grocery
Omnichannel Retail
Automate eCommerce
eCommerce Market Research
Start eCommerce Business
Online Business Consulting
Contact Us
Address
Phone No
Copyright © 2024. Yes to Progress All Rights Reserved. Designed By SEO To Webdesign